Golf-course designers have become concerned that old courses are becoming obsolete since new technology has given golfers the ability to hit the ball so far. Designers, therefore, have proposed that new golf courses need to be built expecting that the average golfer can hit the ball more than 255 yards on average. Suppose a random sample of 166 golfers be chosen so that their mean driving distance is 259.5 yards, with a standard deviation of 44. Conduct a hypothesis test where H0:μ=255 and H1:μ>255 by computing the following: (a) test statistic (b) p-value p= (c) If this was a two-tailed test, then the p-value is
\(\mu=255\\ n=166\\ \bar X=259.5\\ S=44\\ Test \;Stat \;is \;Z\\ Z=\frac{\bar X-\mu}{\left( \frac{S}{\sqrt n} \right)}\\ Z=\frac{259.5-255}{\left( \frac{44}{\sqrt {166}} \right)}\\ Z=1.318\\ \\~\\ H_0:\quad \mu=255\\ H_A:\quad \mu>2.55\\ \\~\\ P(Z>1.318) =P(Z<-1.38) \qquad \text{You can use either}\)
Maybe you have to use a given table.
I like this site.
http://davidmlane.com/hyperstat/z_table.html
\(\boxed{\bf\text {It gives the P value as 0.0938}}\)
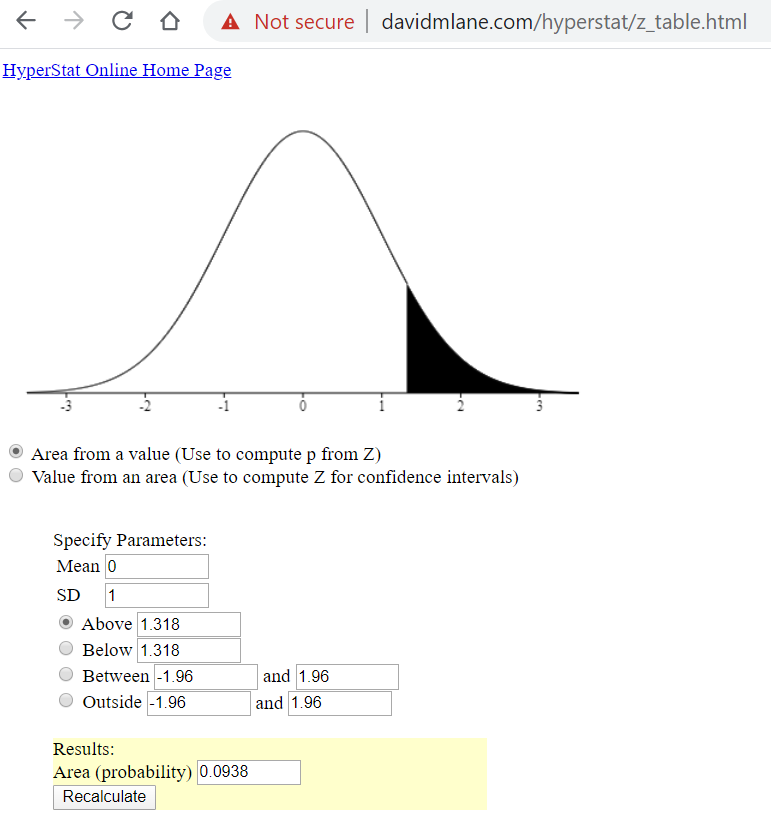
I am reasonably sure that is all correct.
Coding
\mu=255\\
n=166\\
\bar X=259.5\\
S=44\\
Test \;Stat \;is \;Z\\
Z=\frac{\bar X-\mu}{\left( \frac{S}{\sqrt n} \right)}\\
Z=\frac{259.5-255}{\left( \frac{44}{\sqrt {166}} \right)}\\
Z=1.318\\
\\~\\
H_0:\quad \mu=255\\
H_A:\quad \mu>2.55\\
\\~\\
P(Z>1.318)
=P(Z<-1.38)